The human endocrine hormones worksheet answers provide a comprehensive overview of the endocrine system, its hormones, and their roles in regulating various bodily functions. This guide delves into the intricacies of hormone secretion, regulation, and the impact of endocrine disorders, offering a thorough understanding of this vital physiological system.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Endocrine System Basics
The endocrine system is a network of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate a wide range of bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood.
The endocrine system is made up of two main types of glands: endocrine glands and exocrine glands. Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, while exocrine glands secrete their products into ducts that lead to the body’s surface.
There are many different types of hormones, each with its own specific function. Some of the most important hormones include:
- Insulin: Regulates blood sugar levels
- Thyroid hormone: Regulates metabolism
- Growth hormone: Promotes growth and development
- Estrogen and progesterone: Regulate the menstrual cycle and pregnancy
- Cortisol: Regulates stress response
The secretion of hormones is regulated by feedback mechanisms. Negative feedback mechanisms are the most common type of feedback mechanism in the endocrine system. In a negative feedback mechanism, the hormone itself inhibits its own secretion. For example, when blood sugar levels rise, the pancreas secretes insulin.
Insulin lowers blood sugar levels, which in turn inhibits the secretion of insulin.
Major Endocrine Glands
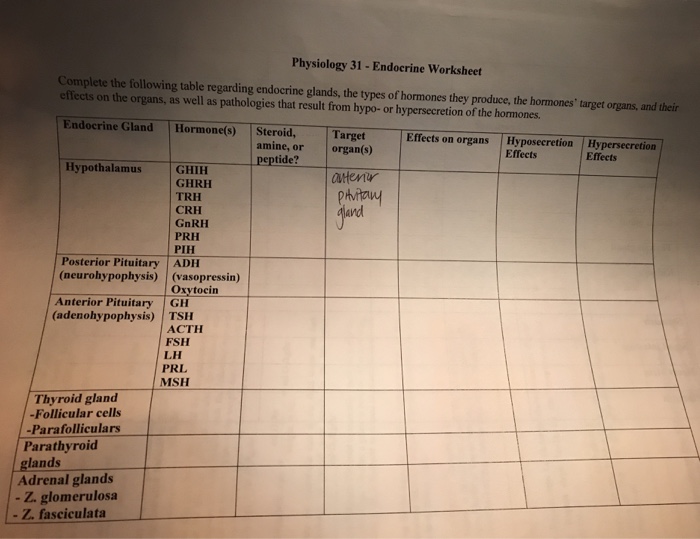
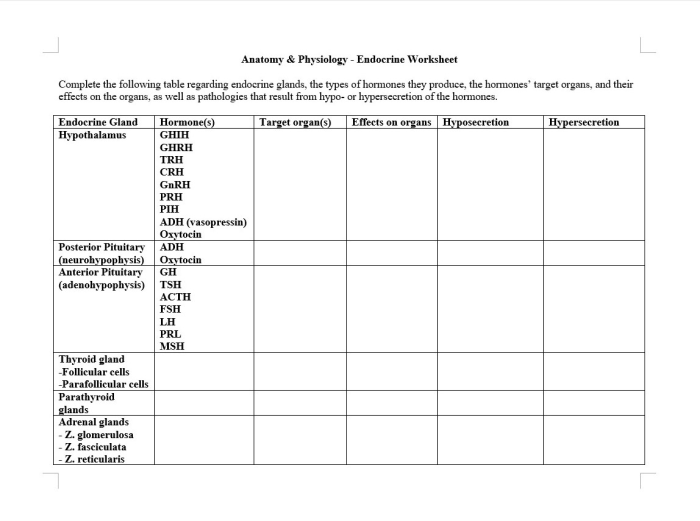
The major endocrine glands include:
| Gland | Location | Hormones Secreted |
|---|---|---|
| Pituitary gland | Base of the brain | Growth hormone, prolactin, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone |
| Thyroid gland | Neck | Thyroid hormone |
| Parathyroid glands | Neck | Parathyroid hormone |
| Adrenal glands | Above the kidneys | Cortisol, adrenaline, noradrenaline |
| Pancreas | Abdomen | Insulin, glucagon |
| Ovaries | Pelvis | Estrogen, progesterone |
| Testes | Scrotum | Testosterone |
Each hormone has a specific target organ or tissue. For example, insulin targets cells in the liver, muscle, and fat tissue. Thyroid hormone targets cells in the brain, heart, and liver.
The endocrine glands work together to maintain homeostasis in the body. Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment despite changes in the external environment.
Hormone Regulation
The secretion of hormones is regulated by a variety of factors, including:
- The hypothalamus
- The pituitary gland
- The target organ or tissue
- The nervous system
- The circulatory system
The hypothalamus is a small region of the brain that plays a major role in the regulation of the endocrine system. The hypothalamus secretes releasing hormones and inhibiting hormones that stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland.
The pituitary gland is a small gland located at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland secretes hormones that stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from other endocrine glands.
The target organ or tissue is the organ or tissue that is affected by a particular hormone. The target organ or tissue secretes hormones that inhibit the secretion of the hormone that stimulated it.
The nervous system and the circulatory system also play a role in the regulation of the endocrine system. The nervous system can stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the endocrine glands. The circulatory system transports hormones throughout the body.
Endocrine Disorders: Human Endocrine Hormones Worksheet Answers
Endocrine disorders are conditions that affect the endocrine system. Endocrine disorders can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Genetic defects
- Autoimmune diseases
- Tumors
- Medications
- Environmental toxins
Endocrine disorders can cause a wide range of symptoms, depending on the gland that is affected. Some of the most common symptoms of endocrine disorders include:
- Weight gain or loss
- Changes in appetite
- Fatigue
- Mood swings
- Sleep problems
- Skin problems
- Menstrual irregularities
- Fertility problems
Endocrine disorders can be diagnosed with a variety of tests, including blood tests, urine tests, and imaging tests. Treatment for endocrine disorders depends on the underlying cause of the disorder.
Clinical Applications
Knowledge of the endocrine system is used in a variety of clinical applications, including:
- The diagnosis and treatment of endocrine disorders
- The development of new drugs and therapies
- The understanding of the role of hormones in health and disease
Hormone replacement therapy is a common treatment for endocrine disorders. Hormone replacement therapy involves taking hormones to replace the hormones that are not being produced by the body.
Endocrine testing is used to diagnose and manage endocrine disorders. Endocrine testing can involve blood tests, urine tests, and imaging tests.
Popular Questions
What are the major endocrine glands and their functions?
The major endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and ovaries/testes. Each gland secretes specific hormones that regulate a wide range of bodily functions, such as growth, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response.
How are hormone levels regulated in the body?
Hormone levels are regulated through feedback mechanisms. Negative feedback loops ensure that hormone levels are maintained within a narrow range. When hormone levels rise above a certain threshold, the feedback loop triggers mechanisms to reduce secretion. Conversely, when hormone levels fall below a certain threshold, the feedback loop stimulates increased secretion.
What are common endocrine disorders and their symptoms?
Common endocrine disorders include diabetes, thyroid disorders, Cushing’s syndrome, and Addison’s disease. Symptoms vary depending on the specific disorder but may include fatigue, weight changes, changes in appetite, and hormonal imbalances.