The subtractive colors gizmo answer key unveils the enigmatic realm of color theory, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding how colors interact and blend in the physical world. Through its insightful explanations and practical examples, this key unlocks the secrets of subtractive color mixing, empowering artists, designers, and anyone curious about the science behind the colors that surround us.
Delving into the fundamentals of subtractive color theory, we explore the concept of primary and secondary colors, the limitations of the RGB color model, and the applications of subtractive color mixing in various industries. By delving into the Gizmo simulation, we gain hands-on experience in mixing colors digitally, solidifying our understanding of how colors interact and produce new hues.
Subtractive Color Theory
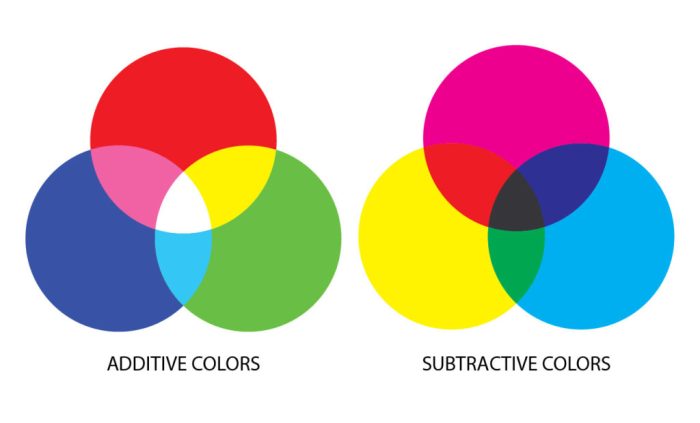
Subtractive color theory is a model that describes how colors are created by mixing light-absorbing pigments. It is used in traditional painting, printing, and other applications where colors are created by mixing physical materials.
The three primary colors in subtractive color theory are cyan, magenta, and yellow. These colors are called “primary” because they cannot be created by mixing any other colors. When these three primary colors are mixed in equal proportions, they create black.
When two primary colors are mixed, they create a secondary color. The secondary colors are green, orange, and purple. When a primary color is mixed with a secondary color, they create a tertiary color. There are six tertiary colors: yellow-green, blue-green, blue-violet, red-violet, red-orange, and yellow-orange.
Examples of Subtractive Color Theory in Use
- Traditional painting
- Printing
- Textile dyeing
- Photography
- Color mixing in computer graphics
Limitations of Subtractive Color Theory, Subtractive colors gizmo answer key
- Subtractive color theory cannot create all colors. For example, it is impossible to create pure white or pure black using subtractive color theory.
- Subtractive color theory is not as accurate as additive color theory. This is because the colors that are created by mixing pigments are not always the same as the colors that are created by mixing light.
- Painting:Subtractive color theory is used by painters to create a wide range of colors by mixing different pigments.
- Printing:Subtractive color theory is used in printing to create images by mixing different inks.
- Textile dyeing:Subtractive color theory is used in textile dyeing to create a wide range of colors by mixing different dyes.
- Photography:Subtractive color theory is used in photography to create images by mixing different light-sensitive chemicals.
- Color mixing in computer graphics:Subtractive color theory is used in computer graphics to create a wide range of colors by mixing different amounts of red, green, and blue light.
The Gizmo Answer Key
The Gizmo answer key provides the correct answers to the questions that are asked in the Gizmo activity. The answers are explained in detail, and additional resources are provided for students who need further clarification.
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| What are the three primary colors in subtractive color theory? | Cyan, magenta, and yellow | These colors cannot be created by mixing any other colors. |
| What is the difference between a primary color and a secondary color? | Primary colors are the three colors that cannot be created by mixing any other colors. Secondary colors are created by mixing two primary colors. | For example, green is a secondary color that is created by mixing blue and yellow. |
| What is the difference between a secondary color and a tertiary color? | Secondary colors are created by mixing two primary colors. Tertiary colors are created by mixing a primary color with a secondary color. | For example, yellow-green is a tertiary color that is created by mixing yellow and green. |
Applications of Subtractive Color Theory
Advantages and Disadvantages of Subtractive Color Theory: Subtractive Colors Gizmo Answer Key
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Can create a wide range of colors | Cannot create all colors |
| Relatively inexpensive | Not as accurate as additive color theory |
| Easy to use | Can be difficult to control the exact color that is created |
General Inquiries
What is subtractive color theory?
Subtractive color theory explains how colors interact when mixed in physical form, such as paints, dyes, or inks. It involves the removal or absorption of light, resulting in the creation of new colors.
How does the Gizmo simulation help in understanding subtractive color theory?
The Gizmo simulation provides an interactive platform to experiment with color mixing digitally, allowing users to visualize the effects of combining different colors and observe how they interact to create new hues.
What are the limitations of subtractive color theory?
Subtractive color theory is limited by the availability of pigments and dyes, which may not always accurately represent the desired colors. Additionally, it is not applicable to digital color mixing, which follows the additive color model.