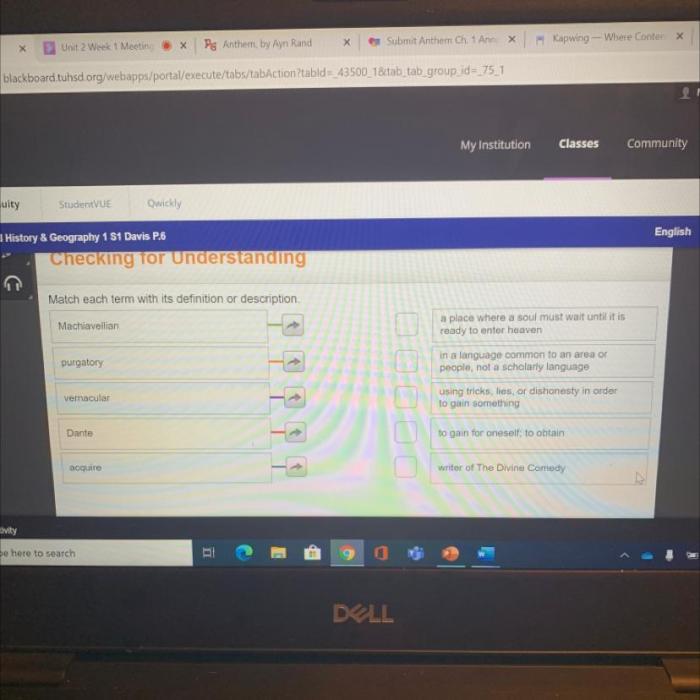
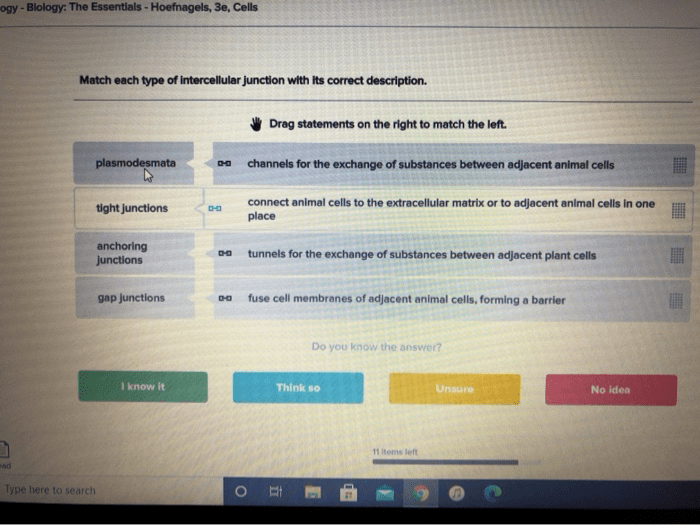
Match each type of intercellular junction with its correct description. Intercellular junctions are specialized structures that connect cells to each other and play a crucial role in maintaining tissue integrity, cell communication, and tissue homeostasis. Different types of intercellular junctions have unique structural and functional characteristics, and understanding their specific roles is essential for comprehending tissue organization and function.
This comprehensive guide provides an overview of the various types of intercellular junctions, their functions, and their significance in cell biology.
Types of Intercellular Junctions
Intercellular junctions are specialized structures that connect cells to each other, allowing them to communicate and coordinate their activities. There are three main types of intercellular junctions: tight junctions, adherens junctions, and gap junctions.
Tight Junctions
Tight junctions are found in epithelial tissues and form a continuous seal between adjacent cells, preventing the leakage of substances between cells. They are composed of proteins that interdigitate with each other from adjacent cells, forming a tight seal that prevents the passage of ions, molecules, and water between cells.
Adherens Junctions
Adherens junctions are found in a variety of tissues and help to maintain cell-cell adhesion. They are composed of transmembrane proteins that bind to each other from adjacent cells, forming a strong adhesion complex that helps to hold cells together.
Adherens junctions are also involved in cell signaling and can transmit signals between cells.
Gap Junctions, Match each type of intercellular junction with its correct description.
Gap junctions are found in a variety of tissues and allow for the direct exchange of ions, molecules, and small molecules between adjacent cells. They are composed of transmembrane proteins that form channels between adjacent cells, allowing for the passage of small molecules between cells.
Gap junctions are important for cell communication and can allow cells to coordinate their activities.
Functions of Intercellular Junctions
Intercellular junctions play a vital role in maintaining tissue integrity and cell communication. Tight junctions prevent the leakage of substances between cells, which is essential for maintaining the proper function of tissues such as the epithelium. Adherens junctions help to hold cells together and can also transmit signals between cells, which is important for coordinating cell behavior.
Gap junctions allow for the direct exchange of ions and small molecules between cells, which is essential for cell communication and coordination.
Matching Exercise
| Type of Intercellular Junction | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Tight Junction | Forms a continuous seal between adjacent cells | Epithelial tissues |
| Adherens Junction | Maintains cell-cell adhesion | Muscle tissue |
| Gap Junction | Allows for the direct exchange of ions and small molecules between adjacent cells | Cardiac muscle |
Commonly Asked Questions: Match Each Type Of Intercellular Junction With Its Correct Description.
What are the main types of intercellular junctions?
The main types of intercellular junctions include tight junctions, adherens junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions, and plasmodesmata.
What is the function of tight junctions?
Tight junctions form impermeable barriers between cells, preventing the leakage of molecules across cell layers.
How do gap junctions contribute to cell communication?
Gap junctions allow the direct exchange of ions, molecules, and electrical signals between adjacent cells, facilitating rapid cell-to-cell communication.