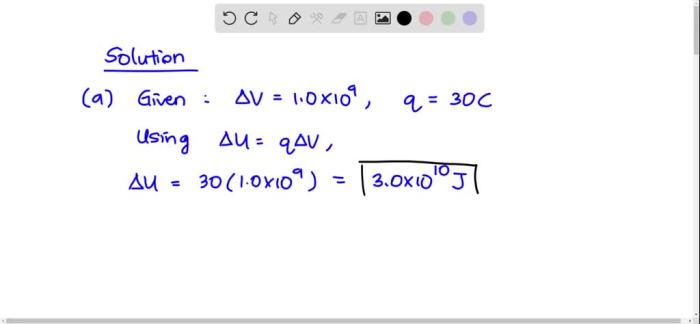
Suppose that in a lightning flash the potential difference, an awe-inspiring natural phenomenon, can reach millions of volts. This immense electrical discharge between the Earth and the clouds, or between two clouds, triggers a cascade of fascinating effects that impact our environment, infrastructure, and scientific understanding.
Delving into the intricacies of potential difference in lightning, we will explore the factors influencing its magnitude, the challenges of measuring this colossal force, and the profound impact it has on our world. By unraveling the mysteries surrounding this electrifying phenomenon, we gain valuable insights into lightning behavior and pave the way for innovative mitigation strategies.
Potential Difference in Lightning Flashes
Lightning is a natural phenomenon that occurs during thunderstorms. It is caused by the buildup of electrical charges in the atmosphere. When the potential difference between two areas of the atmosphere becomes too great, an electrical discharge occurs in the form of a lightning flash.
Factors Influencing Potential Difference in Lightning Flashes
- Distance between the charged areas
- Charge density of the charged areas
- Electrical conductivity of the air between the charged areas
Variation in Potential Difference in Lightning Strikes
The potential difference in lightning flashes can vary greatly depending on the factors mentioned above. In general, lightning flashes that occur between the ground and the clouds have a potential difference of around 100 million volts. However, lightning flashes that occur between two clouds can have a potential difference of up to 1 billion volts.
Measurement of Potential Difference in Lightning
Methods Used to Measure Potential Difference in Lightning Flashes
There are a number of methods that can be used to measure the potential difference in lightning flashes. One common method is to use a lightning rod. A lightning rod is a metal rod that is placed in the ground and connected to a measuring device.
When lightning strikes the lightning rod, the potential difference between the ground and the lightning rod can be measured.
Challenges and Limitations of Measurement Techniques
There are a number of challenges and limitations associated with measuring the potential difference in lightning flashes. One challenge is that lightning flashes are very short-lived, so it can be difficult to get an accurate measurement. Another challenge is that lightning flashes can be very powerful, so it can be dangerous to get too close to them.
Importance of Accurate Measurements
Accurate measurements of the potential difference in lightning flashes are important for understanding lightning behavior. This information can be used to develop better lightning safety measures and to improve our understanding of the atmosphere.
Effects of Potential Difference in Lightning: Suppose That In A Lightning Flash The Potential Difference

Effects on the Environment, Suppose that in a lightning flash the potential difference
The potential difference in lightning flashes can have a number of effects on the environment. These effects include:
- Ground currents: Lightning strikes can cause large currents to flow through the ground. These currents can damage underground infrastructure and can even start fires.
- Electromagnetic pulses: Lightning strikes can also produce electromagnetic pulses. These pulses can interfere with electronic equipment and can even cause power outages.
Potential Impact on Electrical Systems and Infrastructure
The potential difference in lightning flashes can also have a significant impact on electrical systems and infrastructure. Lightning strikes can damage power lines, transformers, and other electrical equipment. This damage can lead to power outages and other disruptions.
Examples of Damage or Disruption
There have been a number of examples of damage or disruption caused by the potential difference in lightning flashes. In 2012, a lightning strike caused a power outage that affected over 1 million people in the northeastern United States. In 2018, a lightning strike caused a fire at a chemical plant in Texas.
The fire caused millions of dollars in damage and forced the evacuation of the surrounding area.
Mitigation of Potential Difference in Lightning

Strategies Used to Mitigate the Effects of Potential Difference in Lightning
There are a number of strategies that can be used to mitigate the effects of potential difference in lightning. These strategies include:
- Lightning rods: Lightning rods are metal rods that are placed in the ground and connected to a building or other structure. Lightning rods provide a path for lightning to travel to the ground, which helps to protect the structure from damage.
- Grounding systems: Grounding systems are networks of wires that are connected to the ground. Grounding systems help to dissipate electrical charges and can help to prevent lightning strikes from causing damage.
Effectiveness of Mitigation Measures and Their Limitations
Lightning rods and grounding systems can be effective in mitigating the effects of potential difference in lightning. However, no mitigation measure is 100% effective. Lightning strikes can still cause damage even if a lightning rod or grounding system is in place.
Examples of Mitigation Measures Implemented in Practice
Lightning rods and grounding systems have been implemented in a variety of settings to protect people and property from lightning strikes. For example, lightning rods are often installed on tall buildings, churches, and other structures that are at risk of being struck by lightning.
Grounding systems are often installed in electrical substations and other areas where there is a high risk of electrical fires.
Applications of Potential Difference in Lightning Research
Contribution to Understanding Lightning Behavior
The study of potential difference in lightning can contribute to our understanding of lightning behavior. By measuring the potential difference in lightning flashes, scientists can learn more about the electrical properties of the atmosphere and the mechanisms that produce lightning.
Potential Applications in Weather Forecasting and Lightning Safety
The research on potential difference in lightning can also have potential applications in weather forecasting and lightning safety. By understanding the factors that influence the potential difference in lightning flashes, scientists can develop better lightning prediction models and lightning safety measures.
Examples of How Potential Difference Measurements Have Been Used to Advance Our Knowledge of Lightning
Potential difference measurements have been used to advance our knowledge of lightning in a number of ways. For example, potential difference measurements have been used to show that the potential difference in lightning flashes can vary greatly depending on the factors mentioned above.
Potential difference measurements have also been used to develop lightning prediction models and lightning safety measures.
Common Queries
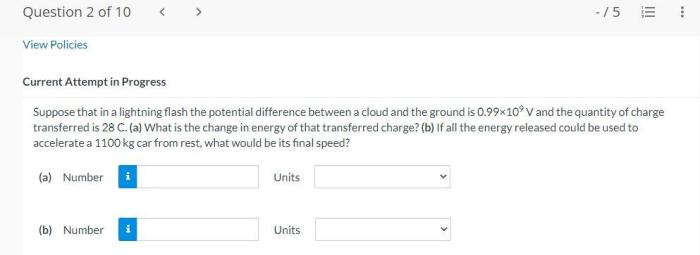
What is potential difference in lightning?
Potential difference in lightning refers to the electrical potential difference between two points in the atmosphere during a lightning strike. It is the driving force behind the massive electrical current that flows through the lightning channel.
How is potential difference measured in lightning?
Measuring potential difference in lightning is a complex task due to its transient nature and the extreme conditions involved. Various techniques are employed, including electric field sensors, magnetic field sensors, and radar systems.
What are the effects of potential difference in lightning?
Potential difference in lightning can have significant effects on the environment, including the generation of ground currents, electromagnetic pulses, and the formation of nitrogen oxides. It can also damage electrical systems, infrastructure, and cause injuries or fatalities.